Mensuration Formulas
Mensuration is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of Geometric shapes, their area, volume and related parameters.
Some important mensuration formulas are:
1. Area of rectangle (A) = length(l) × Breath(b)
2. Perimeter of a rectangle (P) = 2 × (Length(l) + Breath(b))
3. Area of a square (A) = Length (l) × Length (l)
4. Perimeter of a square (P) = 4 × Length (l)
5. Area of a parallelogram(A) = Length(l) × Height(h)
6. Perimeter of a parallelogram (P) = 2 × (length(l) + Breadth(b))
7. Area of a triangle (A) = (Base(b) × Height(b)) / 2
And for a triangle with sides measuring “a” , “b” and “c” , Perimeter = a+b+c
and s = semi perimeter = perimeter / 2 = (a+b+c)/2
And also: Area of triangle =
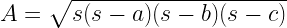
This formulas is also knows as “Heron’s formula”.
8. Area of triangle(A) = 1/2 ab sinC = 1/2 ac sinB = 1/2 bc sinA
Where A, B and C are the vertex and angle A , B , C are respective angles of triangles and a , b , c are the respective opposite sides of the angles as shown in figure below:

area of triangle - mensuration
9. Area of isosceles triangle =

Where a = length of two equal side , b= length of base of isosceles triangle.
10. Area of trapezium (A) =

Where “a” and “b” are the length of parallel sides and “h” is the perpendicular distance between “a” and “b” .
11. Perimeter of a trapezium (P) = sum of all sides
12. Area of rhombus (A) = Product of diagonals / 2
13. Perimeter of a rhombus (P) = 4 × l
where l = length of a side
14. Area of quadrilateral (A) = 1/2 × Diagonal × (Sum of offsets)
15. Area of a Kite (A) = 1/2 × product of it’s diagonals
16. Perimeter of a Kite (A) = 2 × Sum on non-adjacent sides
17. Area of a Circle (A) =

Where r = radius of the circle and d = diameter of the circle.
18. Circumference of a Circle =
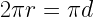
r= radius of circle
d= diameter of circle
19. Total surface area of cuboid =
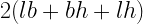
where l= length , b=breadth , h=height
20. Total surface area of cuboid =

where l= length
21. length of diagonal of cuboid =

22. length of diagonal of cube = √3 l
23. Volume of cuboid = l × b × h
24. Volume of cube = l × l × l
25. Area of base of a cone =

26. Curved surface area of a cone = C =

Where r = radius of base , l = slanting height of cone
27. Total surface area of a cone =

28. Volume of right circular cone =

Where r = radius of base of cone , h= height of the cone (perpendicular to base)
29. Surface area of triangular prism = (P × height) + (2 × area of triangle)
Where p = perimeter of base
30. Surface area of polygonal prism = (Perimeter of base × height ) + (Area of polygonal base × 2)
31. Lateral surface area of prism = Perimeter of base × height
32. Volume of Triangular prism = Area of the triangular base × height
33. Curved surface area of a cylinder =

Where r = radius of base, h = height of cylinder
34. Total surface area of a cylinder =

35. Volume of a cylinder =
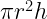
36. Surface area of sphere =
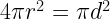
where r= radius of sphere, d= diameter of sphere
37. Volume of a sphere =
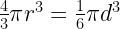
38. Volume of hollow cylinder =
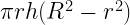
where , R = radius of cylinder , r= radius of hollow , h = height of cylinder
39. Right Square Pyramid:
If a = length of base , b= length of equal side ; of the isosceles triangle forming the slanting face , as shown in figure:

net diagram of right square pyramid
39.a Surface area of a right square pyramid =
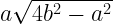
39.b Volume of a right square pyramid =
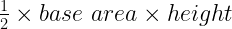
40. Square Pyramid:
40.a. Johnson Pyramid:

- net diagram of johnson pyramid
Volume =
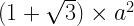
Total Surface Area:
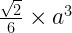
40.b. Normal Square pyramid:
If a = length of square base and h = height of the pyramid then:
Volume =
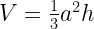
Total Surface Area =

41. Area of a regular hexagon =
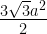
42. area of equilateral triangle =
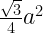
43. Curved surface area of a Frustums =

(h = lateral height)
44. Total surface area of a Frustums =
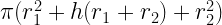
(h= lateral height)
45. Curved surface area of a Hemisphere =
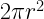
46. Total surface area of a Hemisphere =

47. Volume of a Hemisphere =

48. Area of sector of a circle =
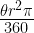
where

= measure of angle of the sector , r= radius of the sector